Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the uterus and, in some cases, the cervix. This procedure is typically performed to treat various gynecological conditions, such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal bleeding, or certain cancers. During TLH, small incisions are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope with specialized instruments is inserted to visualize and dissect the uterus.
The uterus is then removed through the small incisions. TLH offers advantages like reduced post-operative pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional open hysterectomy.

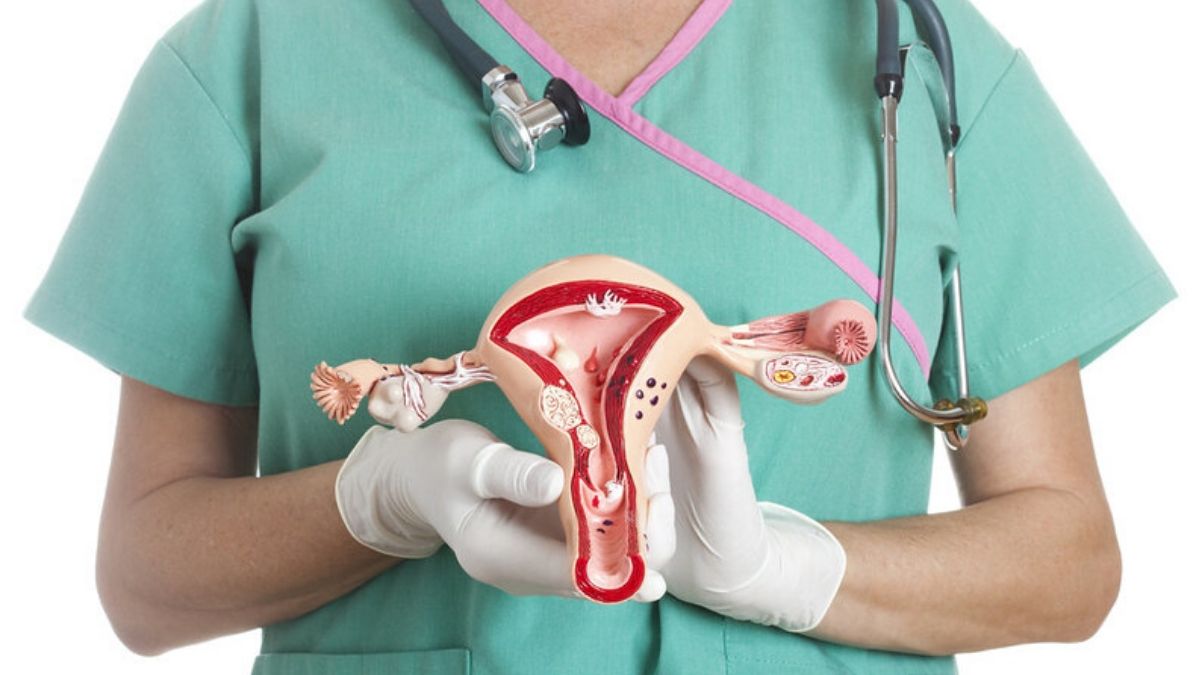
Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic and surgical procedure that involves examining the inside of the uterus using a hysteroscope, which is a thin, lighted tube with a camera. It can be performed for diagnostic purposes to investigate abnormal bleeding, uterine polyps, fibroids, or infertility issues. Additionally, it can be used for therapeutic interventions, such as removing polyps or fibroids, correcting uterine septum, or performing endometrial ablation for excessive menstrual bleeding. Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that is often performed on an outpatient basis, providing a more direct and less invasive approach to diagnosing and treating intrauterine conditions.
Infertility surgeries encompass a range of procedures performed to address anatomical or functional issues that may be causing difficulty in conceiving. Some common infertility surgeries include:
A minimally invasive procedure to remove ovarian cysts that may be affecting fertility.
Removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus to improve fertility.
Surgical interventions to address tubal blockages or abnormalities, such as tubal ligation reversal or tubal cannulation.
As mentioned earlier, hysteroscopy can be used to treat conditions like uterine polyps, fibroids, or septum, which can improve fertility.
Laparoscopic removal of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, which can improve fertility in women with endometriosis.
Infertility surgeries aim to optimize the reproductive anatomy and function, increasing the chances of natural conception or improving outcomes in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). The choice of infertility surgery depends on the underlying cause of infertility and the patient's specific circumstances.
In summary, total laparoscopic hysterectomy, hysteroscopy, and infertility surgeries are minimally invasive procedures that have revolutionized gynecological and reproductive care. They offer benefits like reduced post-operative pain, faster recovery, and improved outcomes, providing patients with less invasive and more effective treatment options for various gynecological conditions and infertility issues.

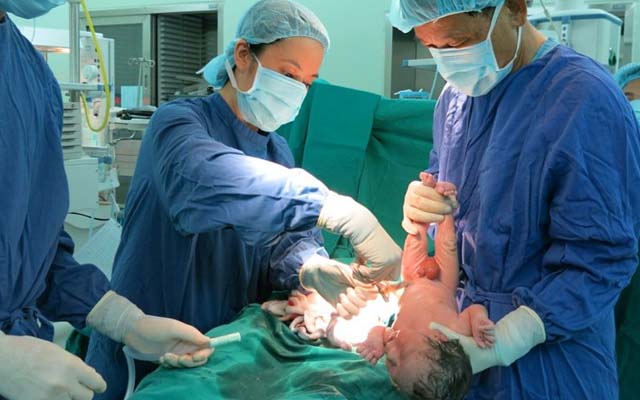
A normal delivery, also known as a vaginal delivery, is the natural process of childbirth where a baby is born through the mother's birth canal. It typically involves the stages of labor, which include dilation of the cervix, the pushing phase, and the delivery of the baby and placenta. This method is preferred when there are no complications or medical reasons that require a cesarean section.
It's important to have proper medical care and support during this process to ensure the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.

A normal delivery with epidural anesthesia is a common approach to manage pain during childbirth. Epidural anesthesia involves injecting pain-relieving medication into the epidural space of the spine. This helps numb the lower half of the body, reducing the pain of contractions while allowing the mother to remain awake and involved in the birthing process. It's a popular choice as it provides effective pain relief, but it's important to discuss the pros and cons with a healthcare provider before making a decision.
LSCS stands for "Lower Segment Cesarean Section." It's a surgical procedure in which a baby is delivered through an incision made in the lower segment of the uterus. This method is used when a vaginal delivery is not possible or safe due to various reasons such as medical complications, fetal distress, or previous cesarean sections. It's also known as a C-section and is performed by medical professionals in a controlled environment to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.